Cigarette smoking is thought to be a major risk factor in various lung diseases including lung cancer and emphysema.
However, the direct effect of cigarette smoke on the viability of lung-derived cells has not been fully elucidated. In this study, we investigated the viability of human lung fibroblast-derived (HFL1) cells to different concentrations of cigarette smoke extract (CSE). CSE induced apoptosis at lower concentrations (10-25%) and necrosis at higher concentrations (50-100%). We also examined the effects of glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1), one of the xenobiotic metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes in the lung, against the cytotoxicity of CSE.
Our results indicated that the level of HFL1 cell death was decreased by transfection with a GSTP1 expression vector and was increased by GSTP1 antisense vector transfection. Therefore, transient overexpression and underexpression of GSTP1 appeared to inhibit and enhance the cytotoxic effects of CSE on HFL1 cells, suggesting that GSTP1 may have protective effects against cigarette smoke in the airway cells
human lung-derived cell; apoptosis; necrosis; xenobiotic enzyme..
FULL TEXT:
http://ajplung.physiology.org/cgi/content/full/280...
Ultimi Articoli

Neve in pianura tra venerdì 23 e domenica 25 gennaio — cosa è realmente atteso al Nord Italia

Se ne va Valentino, l'ultimo imperatore della moda mondiale
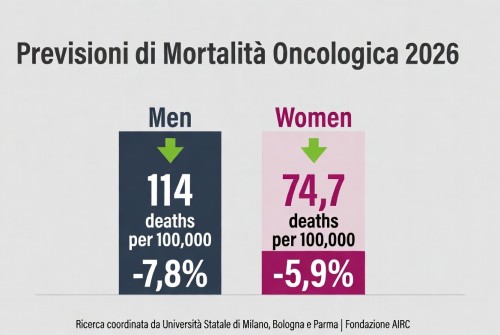
La mortalità per cancro cala in Europa – tassi in diminuzione nel 2026, ma persistono disparità

Carofiglio porta — Elogio dell'ignoranza e dell'errore — al Teatro Manzoni

Teatro per tutta la famiglia: “Inside and Out of Me 2” tra ironia e interazione

Dogliani celebra quindici anni di Festival della TV con “Dialoghi Coraggiosi”

Sesto San Giovanni — 180 milioni dalla Regione per l’ospedale che rafforza la Città della Salute

Triennale Milano — Una settimana di libri, musica, danza e arti sonore dal 20 al 25 gennaio

A febbraio la corsa alle iscrizioni nidi – Milano apre il portale per 2026/2027



